Displaying 681-690 of 893 results

Stewardfish: INSTITUTIONAL ANALYSIS AND ORGANISATIONAL ASSESSMENT OF FISHERIES-RELATED STATE AGENCIES FOR ENABLING ECOSYSTEM STEWARDSHIP IN CARIBBEAN FISHERIES SECTORS
CANARI conducted an Institutional Analysis and Organisational Assessment in each of the project countries to contribute to Outcome 1.2 “Fisheries-related state agencies have capacity to support fishing industry stewardship” and Output 1.2.1 “state agency implementation gaps are assessed regarding support for fisherfolk organisations and their role in stewardship” of the project. The aim of the analysis was to identify current strengths, as well as opportunities for improvement in each project country’s fisheries-related state agencies, in order to improve their capacity to support ecosystem stewardship by fisherfolk and their organisations. The analysis included: • Designing an institutional analysis tool adapted from the Adaptation: Rapid Institutional Assessment (ARIA) methodology, including an organisational assessment survey targeted at the fisheries authorities • Conducting desk studies, surveys, virtual and in-country interviews and focus groups with fisherfolk, fisheries authorities and other key state agencies in the project countries Facilitating national workshops3 to present, validate, refine and receive input on the preliminary findings and identify priorities for improvement, in each project country • Producing country reports of findings, including recommended priorities for improvement This report provides a brief summary of the common findings and recommendations from the institutional analyses and organisational assessments that were conducted in the seven target countries between December to September 2020
 3
3


 Report issue
Report issue
StewardFish: JAMAICA CARIBBEANSPINY LOBSTER VALUE CHAIN ANALYSIS REPORT
The artisanal lobster fishery in Jamaica is classified as “overfished”. It is under significant threat from illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing (IUU), a volatile global market environment and increasing unsustainable fishing practices by the artisanal fishers. Further, it operates as an open-access fishery due to low monitoring and enforcement of effort. Therefore, fishery profits are much less than can be achieved through more stringent controls of the number of trips and/or traps used. Approximately 25 percent of lobsters landed by the artisanal fisher go to export by large industrial fish processors, who export lobsters as a key part of their product line. The exporters sell lobster in a variety of forms including whole raw, frozen; whole cooked, frozen; live and tails, frozen. In 2019, frozen lobsters were exported mainly to France, United States and Hong Kong, respectively. The main Caribbean markets were Barbados, Trinidad and Tobago, and Antigua and Barbuda, respectively. Approximately 75 percent of the lobsters landed by the artisanal lobster fishers go to the hotel and restaurant sector, as lobster is most popularly consumed on beaches, as street food (grilled, boiled or fried) and in local restaurants across the island. Lobsters are normally sold as whole, raw lobsters by the artisanal fishers, or as lobster tails. An excellent new initiative is the introduction of insurance for fishers in March 2021 by Sagicor. This covers group health and life insurance and includes dental, vision, drugs, primary-care, major medical (including surgery) and critical illness. This is a highly-commendable best practice, which reduces income risk and makes fishing a more attractive livelihood option.
 5
5


 Report issue
Report issue
StewardFish: Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Queen Conch Value Chain Analysis Report
The Queen Conch (Strombus gigas) fishery in St. Vincent and the Grenadines (SVG), which previously had declining landings, is now showing rapidly increasing landings and associated exports from 2017 to 2019. This is largely due to increased market access with direct airlift to Miami, as the new Argyle International Airport was opened in 2017. Demand for fresh or frozen conch is low among locals, even though food items such as samosas, conch fritters, and conch and callaloo are available and even exported in small quantities. The ex-vessel prices are showing an overall decline. This is occurring even as the unit export value for conch increased significantly from 2017. This suggests that exporters are receiving an increasing share of the consumer dollar, and that fishers are getting a shrinking share of the foreign consumer dollar. Queen Conch is primarily consumed by tourists locally, as it is relatively more expensive than fish, which is in high demand by locals. The potential for market growth locally will therefore be heavily dependent on conch fishers strengthening links with these buyers to ensure that conch dishes are prominent on their menus. This market potential is also based on tourism growth in St. Vincent. The Fisheries Division provided Hazard Analysis Critical Control Points (HACCP) training to local producers of conch valueadded products (e.g. fritters, samosas), however, government does not provide any direct financial or other support to these processors.
 3
3


 Report issue
Report issue
StewardFish: Stewardship and Livelihoods in Caribbean Small-Scale Fisheries (StewardFish) project CNFO Leadership Institute Pilot Report
The Caribbean Network of Fisherfolk Organisations (CNFO) is a partner with FAO in the implementation of the GEF funded Developing organisational capacity for ecosystem stewardship and livelihoods in Caribbean small-scale fisheries (StewardFish) project. The seven-country project (for Antigua and Barbuda, Barbados, Belize, Guyana, Jamaica, St. Lucia, and St. Vincent and the Grenadines) aims to empower fisherfolk throughout value chains to engage in resource management, decision-making process and sustainable livelihoods, with strengthened institutional support at all levels. The CNFO has made significant progress over the years. However, there is much more to be done to satisfy the development goals of the organisation. Assessments of fisherfolk organisations (FFOs) have highlighted that a number of FFOs are dormant and many others are weak, with limited organisational capacity. The identified weaknesses, include poor management skills, weak leadership, inadequate communication and limited advocacy skills. The CNFO is actively addressing capacity development of its member in these areas. The aim is for members to contribute in a more effective manner to promote sustainable fisheries livelihoods and to participate in fisheries governance. The CNFO is seeking to address the leadership capacity gap by developing a ‘Leadership Institute’. The institute is comprised of four pillars: training, mentoring, forum and a library. This report is delivered for Activity 1.1.1.3 in Component 1, which focuses on “Developing organisational capacity for fisheries governance”. The activity is to “Deliver training, network capacity building with NFOs to form a CNFO 'leadership institute'”
 4
4


 Report issue
Report issue
StewardFish:CARIBBEAN ICT RESEARCH PROGRAMME (CIRP)’S FINAL REPORT Developing Organizational Capacity for Ecosystem Stewardship and Livelihoods in Caribbean Small-Scale Fisheries (StewardFish)
he Developing Organizational Capacity for Ecosystem Stewardship and Livelihoods in Caribbean SmallScale Fisheries (StewardFish) project set out to implement the Caribbean and North Brazil Shelf Large Marine Ecosystems (CLME+) Strategic Action Programme (SAP)1 within Caribbean Regional Fisheries Mechanism (CRFM) Member States. StewardFish is a project of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (“FAO”) with Global Environment Facility (GEF) as financing partner. The project’s aim is to empower fisherfolk throughout fisheries value chains to engage in resource management, decision-making processes and sustainable livelihoods, with strengthened institutional support at all levels. Project countries are Antigua and Barbuda, Barbados, Belize, Guyana, Jamaica, Saint Lucia and St. Vincent and the Grenadines
 4
4


 Report issue
Report issue
Strategic Action Programme for the Sustainable Management of the Shared Living Marine Resources of the Caribbean and North Brazil Shelf Large Marine Ecosystems (CLME+ SAP)
The Strategic Action Programme (SAP) was developed under the CLME Project to provide a comprehensive roadmap towards sustainable living marine resources management through strengthened and consolidated regional cooperation. The SAP combines actions for structural change with capacity building at the regional, national and local levels, and high-priority management interventions and investments on the ground. It puts substantial focus on the strengthening of existing organizations and arrangements for the management of living marine resources, and on the coordination among the organizations and arrangements. This document contains detailed information regarding SAP Strategies and Actions construction, implementation and endorsement by CLME+ Region Countries.
 34
34
 2
2

 Report issue
Report issue
Strategies for Operationalizing Nature-Based Solutions in the Private Sector
Nature-based solutions (NBS) have the potential to address pressing engineering needs while restoring natural landscapes. NBS – sometimes called natural infrastructure and green infrastructure – incorporate the natural environment that mimic or work in concert with natural processes to provide clean water, clean air, flood, fire and drought risk reduction, and other benefits.
 3
3


 Report issue
Report issue
Strategy for mainstreaming EBM-EAF in the CLME+ Region
This strategy is not a separate undertaking. It extracts and summarises the already agreed activities and tasks under all other relevant outputs, but particularly the sub-projects, overall communication strategy and knowledge sharing. Different partners are responsible for these. The field initiatives include UNEP-led EBM sub-project, CRFM-led flyingfish sub-project, OSPESCA-led lobster sub-project, FAO-led shrimp and groundfish sub-project and OECS-led oceanscape that have the potential to practically demonstrate EBM-EAF and document good practices in addition to communicating and conceptualising the practices. The overall governance, sustainable financing, knowledge sharing, research agenda, P-SAP and C-SAP all facilitate institutional mainstreaming. Success will require good leadership in implementing EBM-EAF at all levels, and at all times, in this work and in the institutional arrangements that guide, learn and adapt.
 7
7
 1
1

 Report issue
Report issue
Study on Ocean in the Overseas Countries and Territories (OCTs)
The Overseas Countries and Territories of the European Union (OCTs) make up a group of currently 25 countries and territories which, despite a number of differences between them, have a lot in common (e.g. insular micro-economies, a rich biodiversity, etc.). The Global objective of the study is to provide inputs as a basis for a discussion for the development of an OCTs joint approach to an Ocean Policy by: 1) benchmarking where the OCTs stand - individually - in terms of developing an Ocean agenda as well as their individual contribution to SDG 14 and Aichi targets. To identify the stakeholders responsible for related public policy and/or actions carried in the OCTs; 2) identifying EU and international, public and private, funding opportunities on ocean-related issues, and produce a mapping; 3) identifying topics of interest and common priorities for the OCTs and formulate recommendations to develop a common strategy that may encompasses specific recommendations per geographical area linked to regional strategies and programmes implemented by regional organizations; and 4) providing an overview of other ocean related global and EU initiatives and networks in which OCTA or the OCTs could take part.
 6
6


 Report issue
Report issue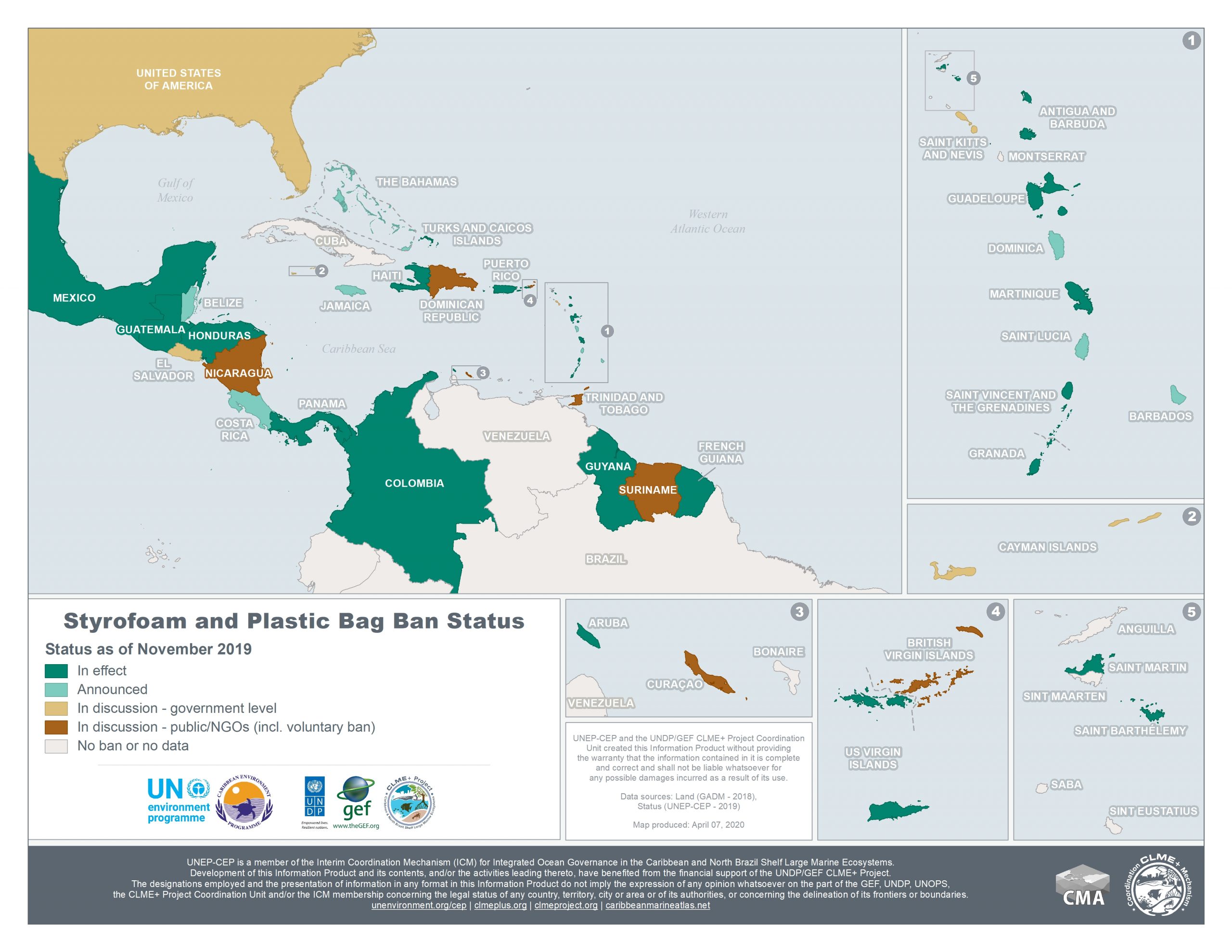
Styrofoam and Plastics Bag Ban Status
To date no abstract has been uploaded for this document
 3
3


 Report issue
Report issue

