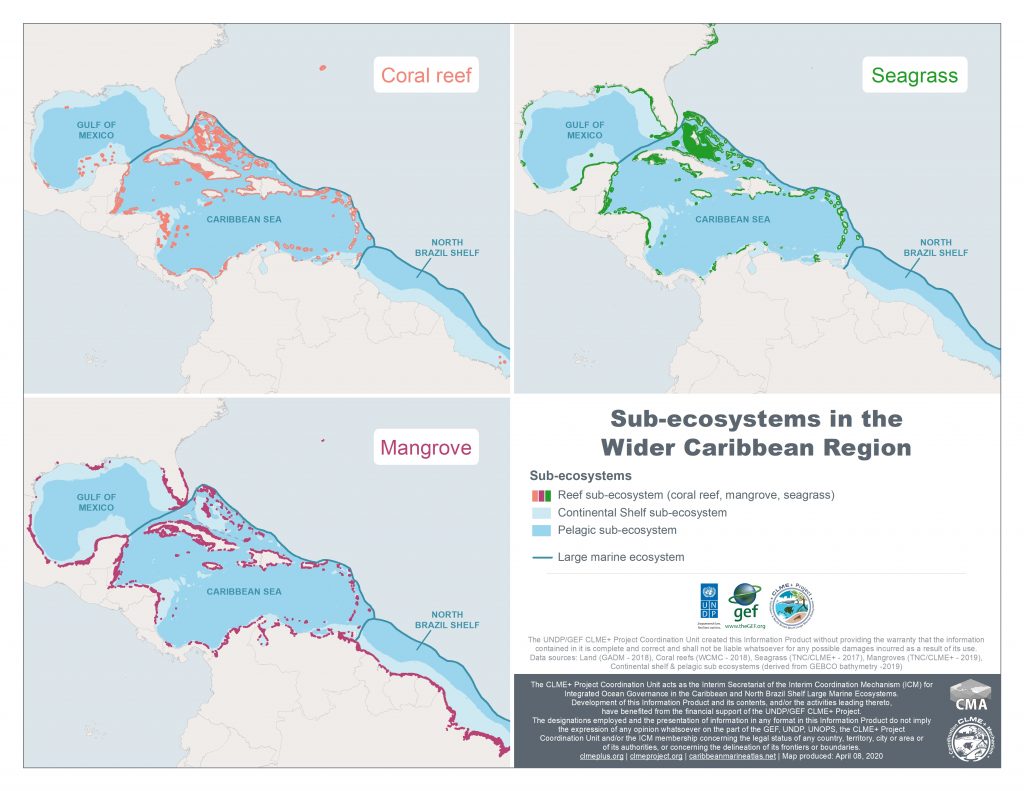
The Wider Caribbean Region, as defined under the “Cartagena Convention” for the Protection and Sustainable Development of the Marine Environment, is composed of 3 Large Marine Ecosystems or LMEs:
- the Gulf of Mexico Large Marine Ecosystem
- the Caribbean Large Marine Ecosystem (CLME)
- the North Brazil Shelf Large Marine Ecosystem (NBLME)
The combination of the latter two LMEs is referred to as the CLME+ region. It is bordered by over 35 States and Territories: the Caribbean & North Brazil Shelf Large Marine Ecosystems. This vast marine area (4.4 million km2) is a major contributor to regional economic development and is key to many globally relevant ecological processes.
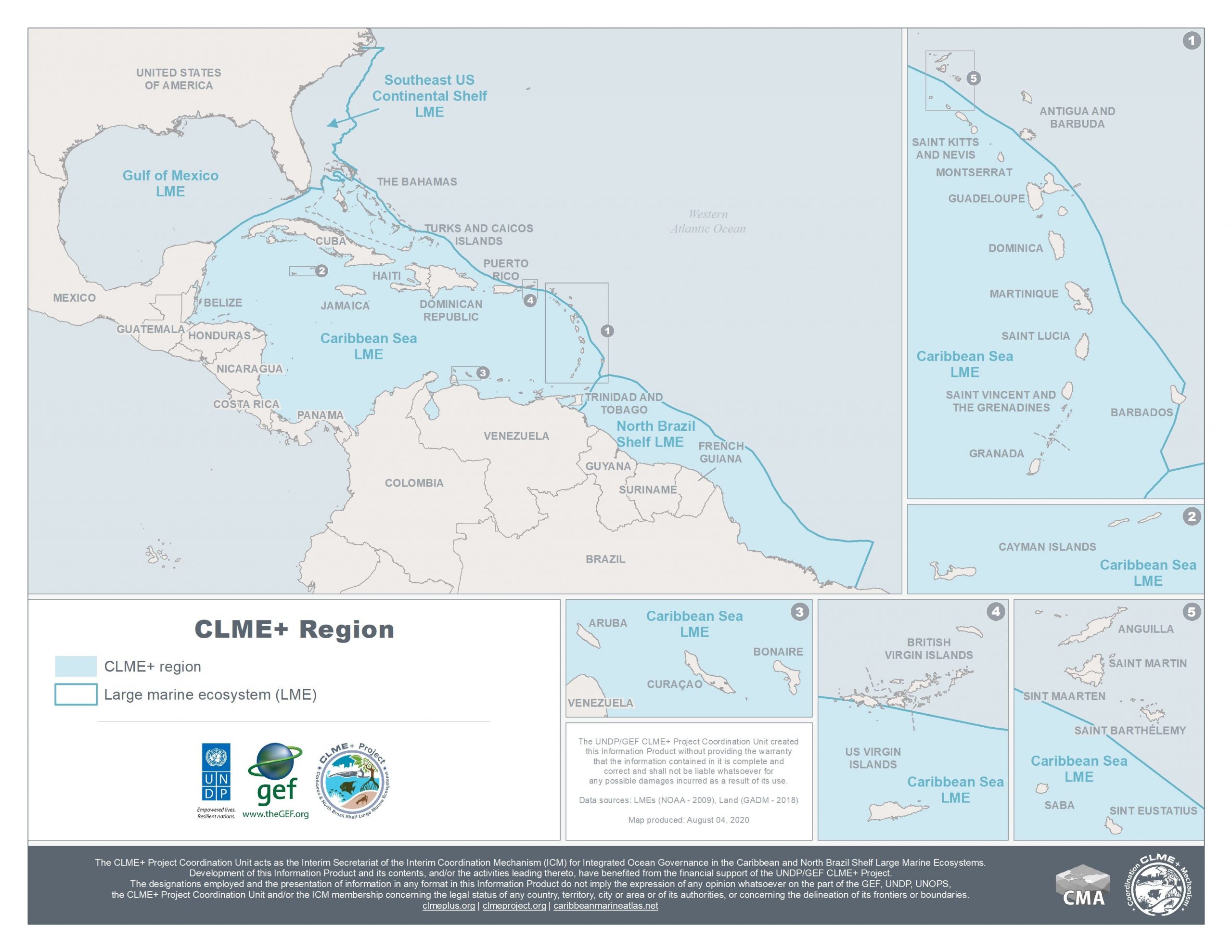
The CLME+ region corresponds to the combined area of the Caribbean and North Brazil Shelf Large Marine Ecosystems. The region is shared by 26 Sovereign States and 18 Overseas Territories.
The CLME+ region is regarded as one of the most geopolitically diverse and complex sets of LMEs in the world. The culturally diverse countries and territories that border this maritime area range from among the largest (e.g. Brazil, USA) to among the smallest (e.g. Barbados, St. Kitts and Nevis) and from the most developed to the least developed in the world.
Both the marine resources as well as key problems affecting these resources (overfishing, pollution, habitat degradation and climate change) are shared to a very large extent by the many territories that make up this region. Highly variable progress exists across the region with regard to ocean and living marine resources governance. Capacities for living marine resources management vary considerably at national, sub-regional and regional levels.